

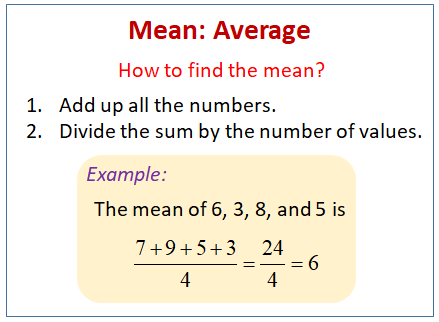
If you have an operation within the absolute value, complete the operation before taking the absolute value. If x is negative, the absolute value is positive. If x is positive, the absolute value is positive. To find the mean, add up all the values in your data and divide by the total number of data points.Ībsolute Value: Absolute value, denoted by two parallel lines | |, is the non-negative value of a real number, x. To understand mean absolute deviation, you also need to know the following terms: For this reason, standard deviation tends to be larger than MAD.

You can think of standard deviation as a weighted average that gives less weight to the values that lie close to the mean and more weight to the data points that lie farther away from the mean. Because calculating standard deviation involves squared deviations, it’s more sensitive to values that are farther away from the mean. As an added step, when calculating standard deviation, you take the square root of the average square deviations to get the units back into their original form.Īlthough standard deviation seems like the clunkier of the two measurements, it’s actually the more common one. When you calculate standard deviation, you square all the deviations, which turns the deviations positive but changes the units of the deviations into squared units. When you calculate MAD, you take the absolute value of the deviations, which turns all the deviations positive. MAD and standard deviations deal with the problem of having positive and negative deviations in different ways. The negative deviations partially or wholly cancel out the positive deviations, and this interferes with the goal of calculating the average deviation. ∑ ( x i − x ˉ ) 2 n − 1 \sqrt \right | ∣ x i − x ˉ ∣), you’ll end up with positive deviations for values that are greater than the mean and negative deviations for values that are less than the mean.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
